Causes and Effects of Obesity
What are the Causes of Obesity?
There is usually not one specific cause for Obesity in patients. Obesity usually involves a combination of causes or risk factors, including;
- Energy Imbalance:
Obesity happens gradually if the amount of energy or calories you consume is more than the amount of energy spent on your daily activities.

- Inactive/Sedentary Lifestyle:
People leading an inactive or sedentary lifestyle are more likely to become obese as they do not burn down the calories they consume. For many of us, physical activity is no longer a part of our daily schedule as we drive to work, instead of walking, we sit at a computer all day at work and work long hours.
- Environmental & Socio-Economic factors:
Lack of safe places for exercising and walking (sidewalks or parks), busy work schedules and larger food portions are all contributing factors to weight gain. Also poor food choices due to lack of education or income ie: eating junk food or fast foods as they are more affordable and readily available and may be marketed as being healthy.
- Family history:
Obesity tends to run in families. The genes inherited from your parents have an effect on the amount of fat stored in your body and your chances of being obese is higher if one or both of your parents are obese. Scientists have discovered several genes, which predispose people to obesity. These genes are the FTO, PCSK1 and ENPP1 genes. This explains why obesity often runs in families and why, for the majority of sufferers, diet and exercise alone are simply ineffective, and patients cannot seem to be able to maintain long term weight loss.
- Excessive Appetite:
It is thought that the hunger regulating part of the brain called the hypothalamus does not function correctly in people with obesity. In these people the hypothalamus continues to stimulate hunger and food desire all the time, even when your body has plenty of energy reserves. This is frequently genetic, and promotes both overeating and poor food choices, and over time leads to obesity.
Another important observation is that people who are constantly hungry often seem drawn toward foods that are rich in calories. Such foods are often high in sugars and fat (such as chocolate, fried foods, and sweets) and lack nutrients.
- Emotional factors:
Unusual eating habits such as excessive eating may occur when experiencing stress or anger. Comfort eating by turning to food to cope with stress, anxiety and low mood is very common. Chocolate, ice-cream, lollies and chips are usually used as they give a temporary 'hit'. Sometimes a serious or traumatic life event may trigger a person to revert back to using food to help feel better. Overeating will cause weight gain.
- Age:
Aging results in muscle loss in the body which is even more if you are inactive. Muscle loss reduces the calorie consumption and consequently uncontrolled diet may increase the chances of becoming obese.
- Disease conditions:
Hormonal disorders such as Hypothyroidism, Cushing’s Syndrome, and Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome may cause weight gain.
- Medicines:
Certain medicines such as Corticosteroids, Antidepressants and Seizure Medications are known to decrease the rate of metabolism, increase your appetite and retain excess water in the body leading to weight gain
What are the Effects of Obesity?
Obesity and excessive weight gain increases your risk of developing serious Chronic Diseases and serious Medical, Physiological and Psychological problems.
At least 80% of people with Obesity will develop at least one weight related medical condition listed below and 60% will develop at least three of these weight related conditions.
These serious conditions associated with Obesity can have a negative impact on your day to day living.
If left untreated, Obesity can lead to premature death.
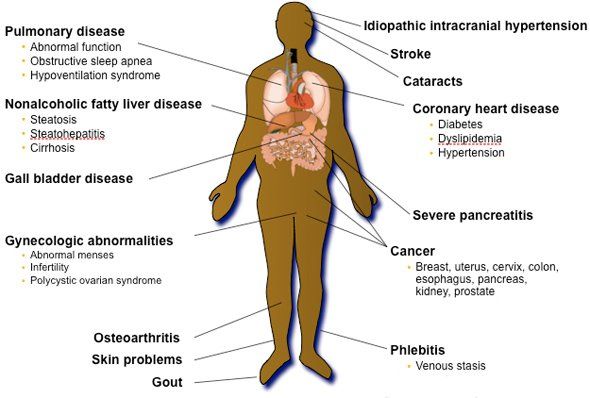
Chronic Diseases and Medical Conditions Caused by Obesity:
| Chronic Diseases and Medical Conditions Caused by Obesity: |
|---|
| Premature death - 50% to 100% increased risk |
| Heart disease |
| Stroke |
| Type 2 Diabetes |
| High Blood Pressure |
| High Cholesterol |
| Cancer (breast, uterine, colon, pancreas, liver, prostrate, oesophagus,endometrial, kidney, thyroid ) |
| Fatty Liver Disease |
| Sleep Apnoea |
| Arthritis |
| Pregnancy complications |
| Gall bladder complications |
| Urinary incontinence |
| Digestive disorders (gastroesophageal reflux disease) |
Effects of Obesity on Psychological and Social Well-Being:
- Low confidence/self-esteem & Negative self-image
- Social isolation
- Discrimination
- Anxiety
- Depression
Effects of Obesity on Day-to-Day Living:
- Normal tasks become harder as difficult to move around
- Feeling tired all the time and tiring quickly
- Shortness of breath
- Joint pain (especially weight bearing knees & hip joints)
- Back Pain
- Snoring
- Public transport seats, aeroplane seats and cars may be too small for you
- You may find it difficult to maintain personal hygiene
Read more about our Professional Health Management Program
Contact Us
Make an Appointment
FOOTER - Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later
Let us take care of you
Dr Michael Hatzifotis • Surgery Brisbane • All Rights Reserved